Prolaborate Data Modelling support to customize the forms
Prolaborate Data Modelling support to customize the forms
Written by GUILLAUME FINANCE
Data Models generated via a reverse engineering from an existing Database in Enterprise Architect modelling tool can be shared dynamically with Prolaborate web solution. This can be useful to provide access to an existing Physical Data Model or “work in progress” database redesign views, and gather feedback via Prolaborate collaborative features (discussions, reviews, etc.).
Sparx Enterprise Architect (EA) data models support tables and columns, views, stored procedures, functions from all major DBMS (SQL server, MySQL, Postgres, etc.). This is achieved with built-in stereotyped UML classes, attributes and operations.
When such information is shared outside Enterprise Architect tool, it is important to customize or hide unnecessary details for the target users.
Prolaborate Modeling Language feature is ideal to achieve this via custom profiles and a form designer. Built-in Prolaborate languages are available for UML, BPMN, or Archimate elements (SysML is available on request). If you use your own stereotypes, the MDG XML file used for Enterprise Architect can also be imported in Prolaborate. When it comes to Data Modelling, I found that Prolaborate doesn’t currently support this definition. Since data models are built in EA, there isn’t any MDG XML file available to manually import. Hence my only option was to recreate a Data Modelling MDG in EA solely for the purpose of configuring Prolaborate web solution.
Below is an illustration of how it works with Sparx EA Example project.
Note: this MDG definition has been submitted to Prolaborate team and will be available to download, before it is included in Prolaborate future releases. In the meantime you can contact me on guillaume[at]umlchannel.com to get a copy.
Initial Context
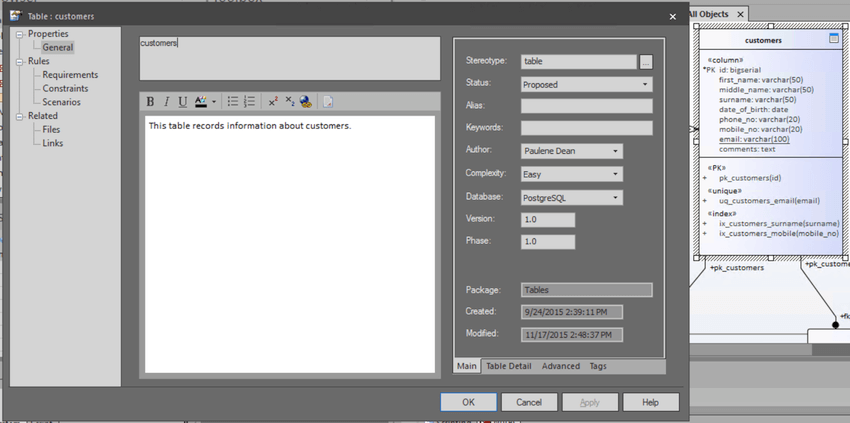
To illustrate the advantage of using Modelling Languages, the following screenshot shows how the details of a table is rendered in Prolaborate:
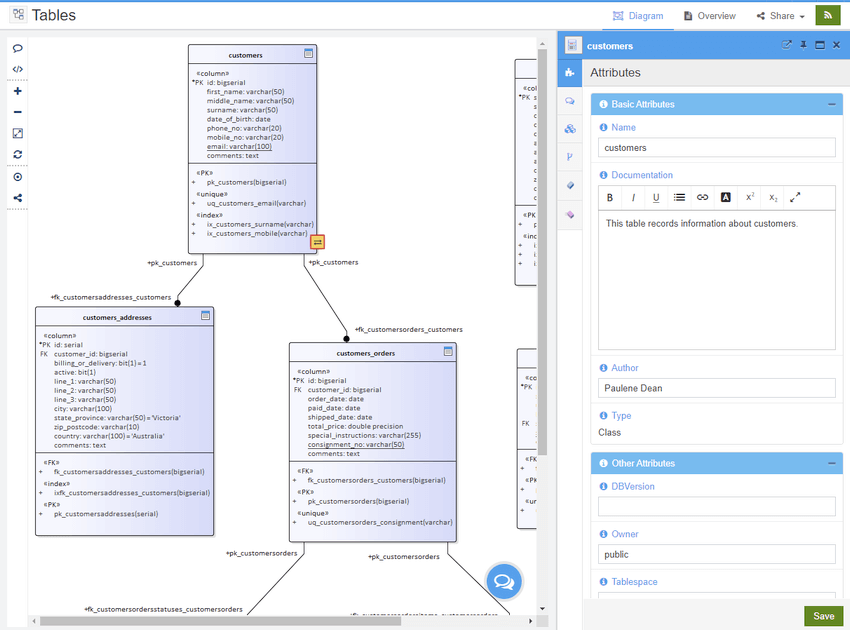
The default table element details are displayed with all tagged values. Not only some of these fields may not be relevant, but also note the field Type mentions that it’s a Class; where this element is rightly a “table” stereotyped UML class, this information to an end user can be rather confusing!
The aim of installing and configuring of the Data Model Modelling Language is to have the ability manage the visible and hidden information amongst the element fields (e.g. name, notes, author, modified date, etc.) or custom tagged values, and rename their label when needed.
Important: Prolaborate doesn’t currently support customization of attributes and operations from a Modeling Language profile. Hence table columns and constraints cannot currently be customized.
Install the Data Model Modelling Language
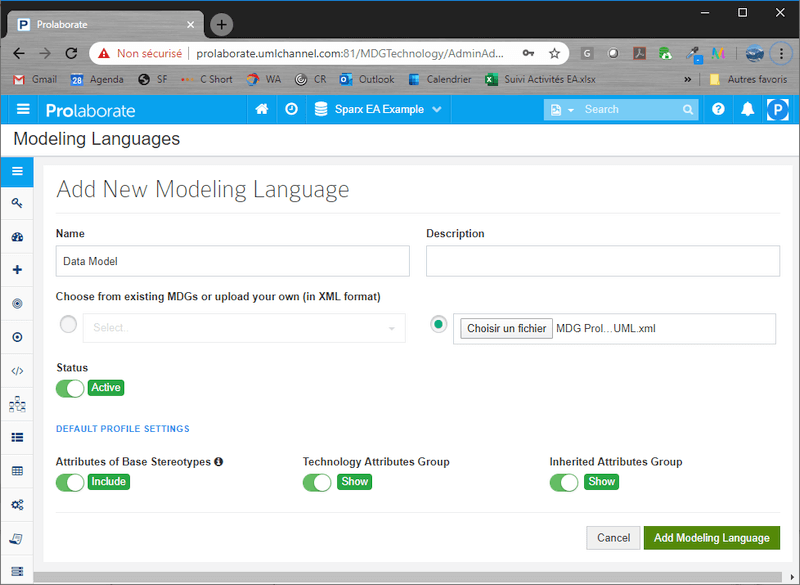
- Once logged in, open Prolaborate Repository configuration, and select Modelling Languages

- Fill in the form, select the provided MDG Prolaborate EAUML.xml file, and click on Add Modeling Language
- The Data Model custom language is installed and ready to be configured.
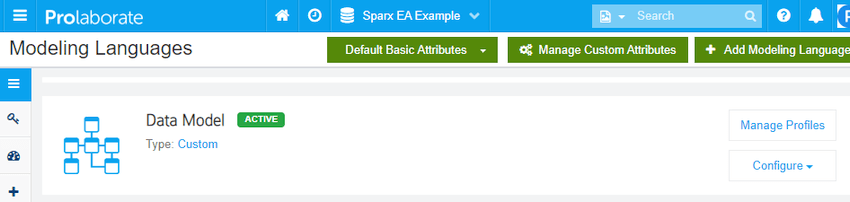
Customize the users’ views with profiles
Below is an illustration to customize the fields for a DB table.
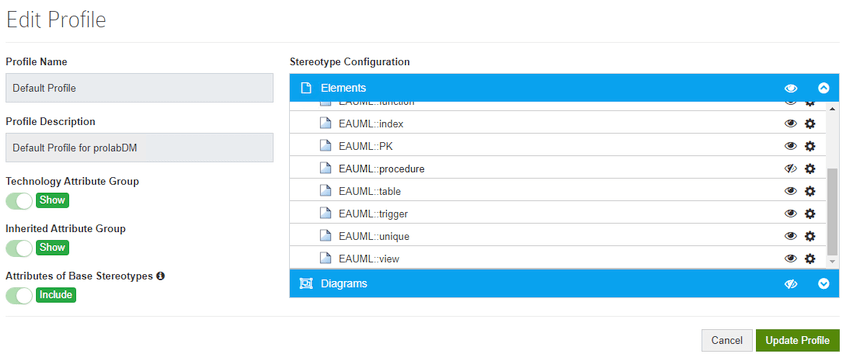
- Click on Manage Profiles
- Create a new profile or edit the default one
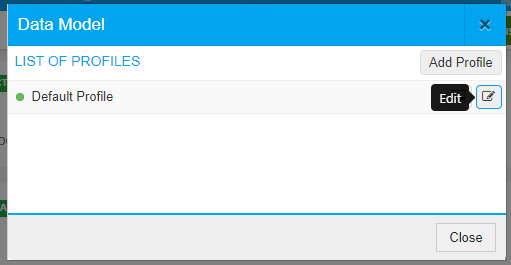
- The data model stereotypes are listed e.g. table, column, view, trigger, etc.
Note: the eye icon can be used to hide all elements under the selected stereotype to be hidden e.g. views and stored procedures.
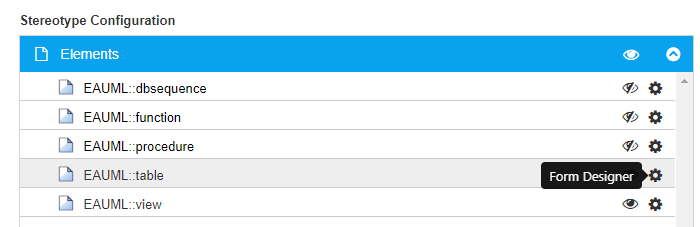
- Open the form designer to customize the visible fields for a given stereotype e.g. table.
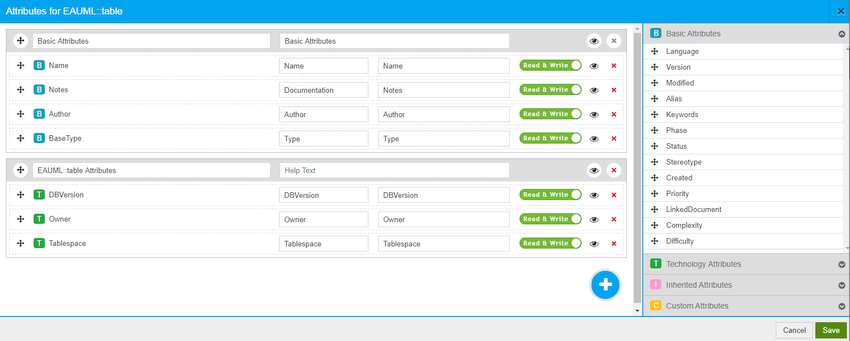
- The initial configuration is illustrated below.
- The table name, notes, author and type (e.g. Class) are listed under the Basic Attributes.
- All three tagged values are listed under EAUML::table Attributes
- These fields can removed, hidden, made read-only, or renamed. Other fields can be added (see the lists on the right hand side).
- The element’s EA fields (e.g. name, notes, alias, etc.) can be freely mixed with tagged values, within any group.
- The order can be updated as needed.
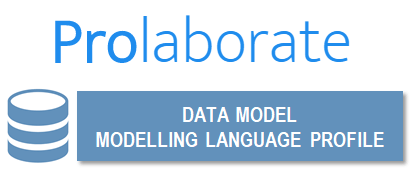
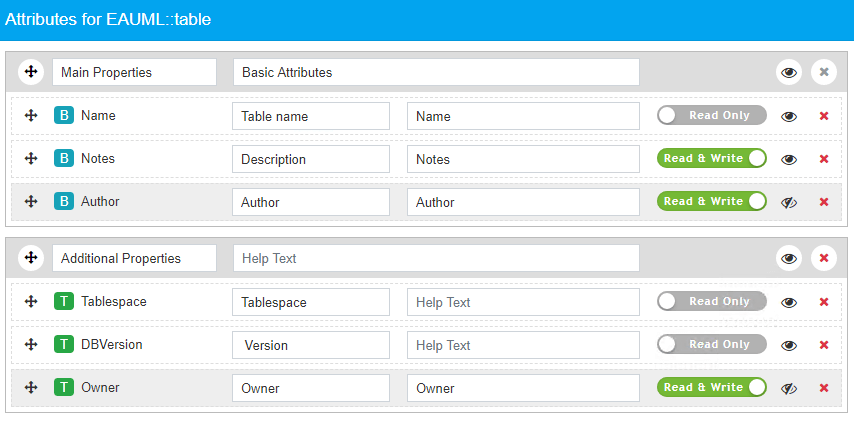
- The example below matches the following configuration:
- The fields’ group titles have been renamed to Main Properties (from Basic Attributes) and Additional Properties (from EAUML::table Attributes).
- The table name field is read-only and available against the label “Table name”.
- The table notes is visible against the “Description” label, and can be updated if the user has the write permission.
- The Type field has been removed.
- The Author field is not visible.
- Only Tablespace and DBVersion tagged values are visible in read-only mode.
Important – in theory, a table index constraint can be customised as illustrated here. However Modelling Language profiles are not yet supported by Prolaborate for attributes and operations (all columns and constraints remain visible). This is a possible enhancement for Prolaborate team to consider in a future release.
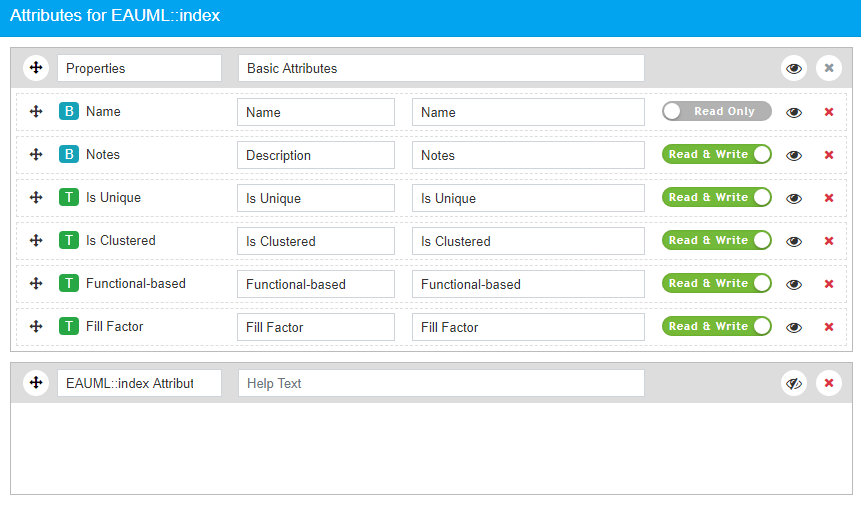
- The Profile can be saved.
Note: further details are available from Prolaborate online help .
User experience
Accessing the same physical data model, the displayed information matches the new table profile definition: